Are you drowning in digital files and paper clutter? From overflowing inboxes to chaotic cloud storage, manually organizing documents is a soul-crushing chore. The constant worry about compliance, the wasted hours searching for a single contract, and the nagging fear of losing critical information are huge pain points that drain your time and energy.
This manual disorganization doesn’t just create stress; it kills productivity. But what if there was a better way? Imagine a system where files organize themselves, compliance is nearly effortless, and you have complete peace of mind knowing everything is in its right place. This isn’t a fantasy—it’s the result of implementing a robust document retention policy.
In this guide, we’ll unveil eight essential document retention policy best practices that transform chaos into order. We’ll provide actionable insights and practical examples, showing you how to leverage smart strategies and AI to automate the process, save countless hours, and achieve organizational Zen. You’ll learn exactly how to build a system that manages itself, so you can focus on what truly matters.
1. Implement a Classification System
A document retention policy is only as effective as your ability to apply it consistently. The foundation for this consistency is a robust document classification system. This framework organizes your records into logical categories based on their content, sensitivity, and regulatory requirements, assigning a specific retention schedule to each category. This eliminates guesswork and ensures that every document, from a simple invoice to a sensitive legal contract, is managed correctly, saving you time every day.
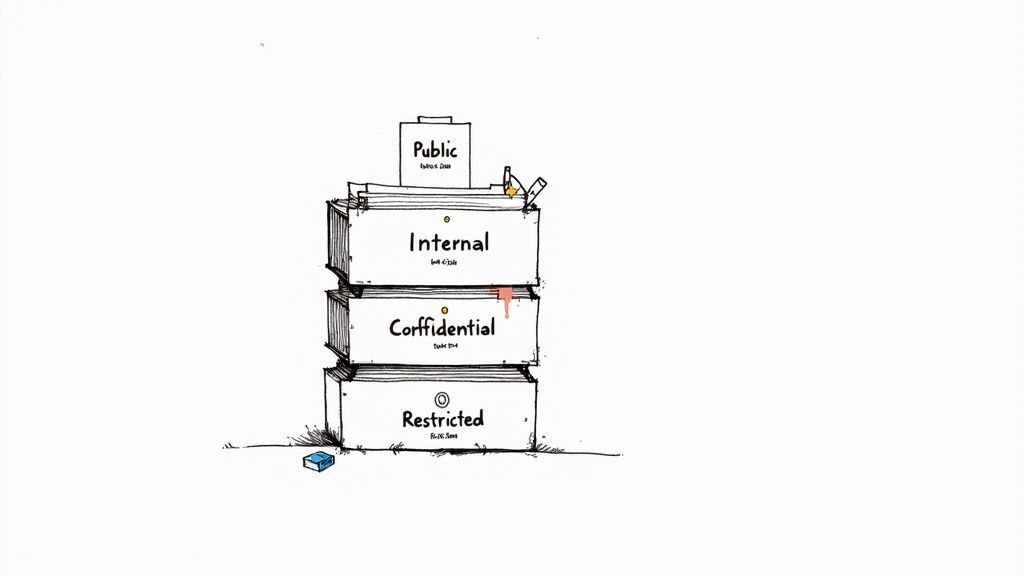
The old manual way—letting employees guess how long to keep records—leads to chaos, compliance risks, and wasted storage space. A clear system, powered by AI, brings order and peace of mind. It transforms your data management from a liability into a streamlined asset.
How to Get Started
Start by defining broad categories and then add layers of detail. A common approach is to classify documents by both type (e.g., Financial, HR, Legal, Marketing) and sensitivity (e.g., Public, Internal, Confidential, Restricted).
- Example 1 (Healthcare): A hospital might classify patient records as “Confidential Health Information” with a retention period mandated by HIPAA, while classifying marketing brochures as “Public” with a much shorter, event-based retention schedule.
- Example 2 (Finance): A financial advisory firm would classify client trade confirmations under “SEC Records” with a strict six-year retention period, separate from internal meeting minutes classified as “General Business Records.”
Key Insight: A well-designed classification system is a core component of effective document retention policy best practices. It directly translates legal and business rules into actionable, everyday procedures for your team.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
- Start with High-Risk Categories: Begin by classifying documents with the most significant legal or financial implications, like tax records, employee files, and contracts.
- Use Consistent Naming: Establish a clear and uniform naming convention for all files and folders to prevent confusion and make retrieval simple.
- Involve Key Stakeholders: Collaborate with legal, compliance, IT, and department heads to ensure your classification scheme meets everyone’s needs and compliance obligations.
- Automate When Possible: Leverage modern AI tools for intelligent document organization to automatically tag and classify incoming files, saving significant time and eliminating human error.
2. Establish Clear Retention Schedules
Once you’ve classified your documents, the next step is to define exactly how long to keep each category. Establishing clear retention schedules is the engine of your policy, dictating the lifecycle of every record from creation to secure disposal. These schedules are not arbitrary; they are precise timelines based on a combination of legal requirements, industry standards, and business operational needs.
Without defined schedules, documents are either kept indefinitely—creating a mountain of digital and physical clutter—or deleted prematurely, exposing your organization to severe legal and financial penalties. A well-researched schedule removes ambiguity, ensuring you meet compliance obligations while simultaneously freeing up valuable storage resources and minimizing risk. This proactive approach brings clarity and peace of mind to your data management strategy.
How to Get Started
Begin by researching the specific laws and regulations that govern your industry and location. This creates the mandatory minimum retention periods for key document types. From there, consider your own business needs, such as the statute of limitations for potential lawsuits or operational requirements for accessing historical data.
- Example 1 (Healthcare): Under OSHA regulations, employee exposure and medical records must be kept for the duration of employment plus 30 years, a much longer period than standard HR files.
- Example 2 (Finance): A brokerage firm must adhere to SEC Rule 17a-4, which mandates a six-year retention period for specific records like trade blotters and ledgers, with the first two years in an easily accessible format.
- Example 3 (General Business): The IRS generally requires tax-related records to be kept for three to seven years, depending on the specifics of the return, making this a critical schedule for any business.
Key Insight: Clear retention schedules are a cornerstone of effective document retention policy best practices because they provide the non-negotiable rules for data disposal, turning complex legal requirements into a simple, actionable calendar.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
- Consult with Legal Counsel: Work with legal experts to validate your retention schedules against all relevant federal, state, and industry-specific regulations.
- Create a Retention Matrix: Develop a simple, easy-to-read chart or spreadsheet that lists document categories, their corresponding retention periods, and the legal citation or business reason for the schedule.
- Build in Automated Alerts: Use your document management system to set up automatic reminders for when records are nearing the end of their retention period and are eligible for disposal review.
- Document Your Reasoning: For each schedule, record why the specific period was chosen. This documentation is invaluable during an audit or legal inquiry.
3. Automate Document Lifecycle Management
Manually tracking retention schedules for thousands of documents is a productivity nightmare and a recipe for error. Automating the document lifecycle with AI removes this burden, using technology to manage records from creation to disposal based on your predefined policy. This ensures rules are applied consistently and accurately without constant human intervention.
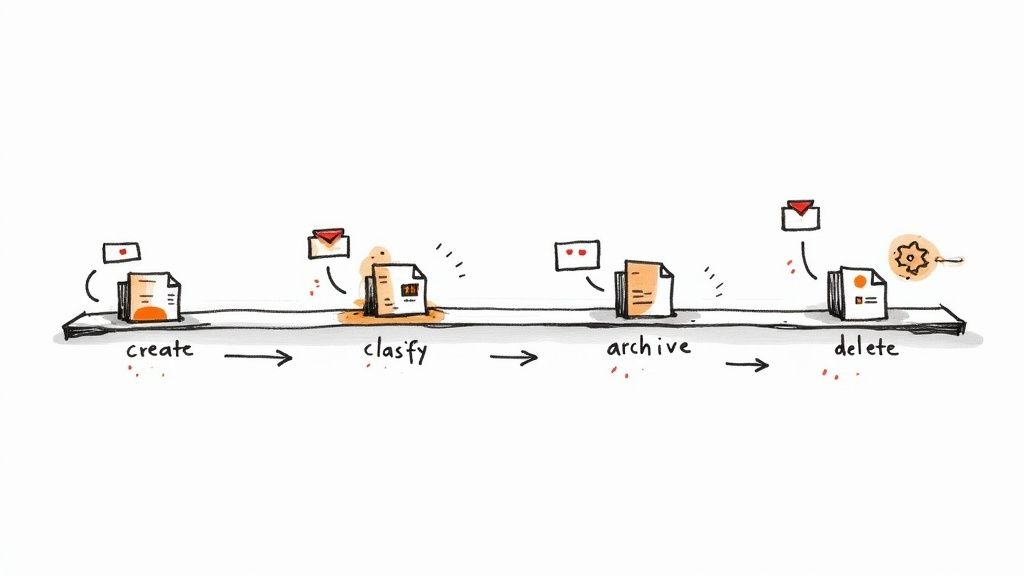
This modern approach transforms your policy from a static document into an active, intelligent system. It saves countless hours, minimizes the risk of accidental deletion, and gives you peace of mind knowing your compliance obligations are being met automatically in the background.
How to Get Started
Modern document management systems offer powerful AI-driven automation. You can set up rules that automatically apply retention labels based on a document’s type, content, or storage location. The system then tracks the retention period and can initiate a review or securely delete the file when its time is up.
- Example 1 (Microsoft 365): A company can create a retention policy in Microsoft 365 that automatically labels all documents uploaded to a specific SharePoint folder named “Financial Audits” with a seven-year retention period, after which they are flagged for final review by the finance manager.
- Example 2 (AI-Powered DMS): An AI tool like Fileo can scan an incoming invoice, automatically name it “VendorName_Invoice_Date,” file it in the “Accounts Payable” folder, and apply a seven-year retention tag—all without a single click. This is the ultimate time-saver.
Key Insight: Automation is the most reliable way to enforce your document retention policy at scale. It bridges the gap between policy creation and practical, everyday execution, making consistent compliance an achievable goal.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
- Start with a Pilot Program: Test your automation rules on a single department or document category, like HR onboarding forms, to work out any issues before a company-wide rollout.
- Test Rules Thoroughly: Before going live, rigorously test your automated workflows to ensure they classify, retain, and dispose of documents as intended.
- Provide Comprehensive Training: Ensure employees understand how the automated system works and what their role is, especially if manual approvals are part of the process.
- Regularly Audit Automated Actions: Periodically review logs and reports to verify that the system is performing correctly and to identify any anomalies in retention actions. Learn how to unlock your organization’s potential with document management automation for peak productivity.
4. Develop a Comprehensive Written Policy
A retention schedule is just a set of rules, but a written policy transforms those rules into a formal, organization-wide standard. This foundational document outlines procedures, assigns responsibilities, and clearly communicates expectations to every staff member. It serves as the single source of truth for how your organization handles its records, eliminating ambiguity and providing a defensible framework for your actions.
Without a formal policy, retention practices become inconsistent and reliant on individual habits, exposing your business to significant compliance risks and operational chaos. A clear, written policy provides the structure needed to manage records effectively, ensuring everyone understands their role in protecting company information and saving valuable time trying to figure out the right procedures.
How to Get Started
The policy should be more than a list of retention periods; it needs to be a practical guide. It should define key terms, state the policy’s purpose, and detail the procedures for retaining, archiving, and destroying documents across all departments and formats, both physical and digital.
- Example 1 (Healthcare): Mayo Clinic’s extensive retention standards are formally documented to ensure every employee, from administrative staff to clinicians, understands their specific obligations under HIPAA and other healthcare regulations.
- Example 2 (Technology): Google’s publicly available data retention and privacy policies clearly document for both employees and users how different types of data are managed, how long they are kept, and the rationale behind those decisions.
Key Insight: A formal written policy is a critical element of document retention policy best practices because it converts abstract legal requirements into clear, enforceable, and repeatable business processes.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
- Use Plain Language: Avoid legal jargon. Write the policy in simple, clear terms that non-technical staff can easily understand and follow.
- Designate a Policy Owner: Assign a specific individual or department (e.g., Compliance Officer) to be responsible for maintaining, reviewing, and updating the policy.
- Include a Scope and Purpose: Clearly define which records, departments, and employees the policy applies to and why it is important.
- Make It Accessible: Post the policy on the company intranet or another central, easily accessible location for all employees.
- Obtain Formal Approval: Ensure the policy is reviewed and signed off on by legal, compliance, and executive leadership before it is distributed.
5. Implement Regular Employee Training and Awareness
A document retention policy is only effective if your team understands and follows it. Ongoing, mandatory training programs are essential to bridge the gap between policy creation and everyday practice. This ensures every employee, from entry-level staff to senior management, understands their specific responsibilities, the reasons behind the rules, and the serious consequences of non-compliance.
Without consistent training, even the best policy will fail, leading to accidental data breaches, compliance failures, and legal risks. Regular education transforms your policy from a static document into a living, breathing part of your company culture, empowering employees to become the first line of defense in protecting sensitive information and boosting their own productivity.
How to Get Started
Develop a training curriculum that is role-specific and easy to understand. The goal is not just to inform but to build a culture of compliance where proper document handling is second nature.
- Example 1 (Healthcare): A hospital could implement mandatory annual HIPAA training for all staff, focusing on the specific retention rules for patient charts, billing records, and administrative documents to ensure patient privacy and regulatory adherence.
- Example 2 (Finance): A financial services firm might require employees to complete interactive training modules on SEC and FINRA regulations, including quizzes that test their knowledge of retaining trade confirmations, client communications, and audit trails.
Key Insight: Consistent training is one of the most critical document retention policy best practices because it turns passive rules into active, responsible behaviors across your entire organization.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
- Make It Mandatory: Require all relevant employees to complete the training and track completion rates to ensure 100% participation.
- Use Real-World Scenarios: Tailor training content with examples specific to different departments, such as how the marketing team should handle campaign data versus how HR should manage personnel files.
- Vary Your Methods: Combine online modules, in-person workshops, and quick video refreshers to keep the content engaging. For further insights on developing effective programs, consider these employee training best practices.
- Test and Reinforce: Use quizzes to test knowledge retention and send out regular email tips or reminders about key aspects of the policy.
6. Conduct Regular Compliance Audits and Reviews
A document retention policy is not a “set it and forget it” tool. To ensure it remains effective and compliant, you must regularly verify that it is being followed correctly across the organization. Conducting periodic audits and reviews is the mechanism for this verification, allowing you to assess compliance, identify weaknesses, and confirm that documents are managed according to your established procedures.
This process transforms your policy from a document sitting on a shelf into a living, operational framework. Without regular audits, even the best policy can fail due to human error, outdated procedures, or technological gaps, exposing your business to significant legal and financial risks. Audits provide the necessary accountability and a clear path for continuous improvement, giving you peace of mind.
How to Get Started
Begin by establishing a regular audit schedule, such as annually or semi-annually. The audit’s goal is to sample records from various departments and compare their management against the policy’s rules. This involves checking if files are stored correctly, retained for the proper duration, and disposed of securely.
- Example 1 (Healthcare): A hospital might conduct a HIPAA compliance audit, pulling a sample of patient records to verify that they are stored securely and that access logs are complete, ensuring they meet the mandated retention and privacy requirements.
- Example 2 (Finance): A public company preparing for a SOX audit would review its financial record-keeping processes, confirming that invoices, expense reports, and financial statements are retained accurately and are readily accessible for the required seven-year period.
Key Insight: Regular audits are a critical component of document retention policy best practices, serving as a feedback loop that ensures your policy is not just a plan, but a reality.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
- Schedule Audits Strategically: Plan audits during predictable, slower business periods to minimize disruption to daily operations.
- Use Standardized Checklists: Create a consistent audit checklist to ensure every department is evaluated using the same criteria, from file naming to disposal protocols.
- Document Everything: Maintain detailed records of all audit activities, including the scope, findings, and any discussions with staff.
- Assign Clear Remediation Tasks: When gaps are found, assign specific corrective actions to individuals or teams with clear deadlines to ensure accountability.
- Consider Third-Party Audits: For high-stakes compliance areas like GDPR or SEC regulations, an external audit can provide an unbiased assessment and greater credibility.
7. Integrate Legal Hold and Litigation Support Procedures
When litigation is anticipated or ongoing, your standard document retention schedule must be suspended for all relevant records. A legal hold (or litigation hold) is a formal process that overrides normal retention and disposal procedures to preserve potentially relevant information. Integrating clear legal hold protocols into your policy is essential to avoid accusations of evidence spoliation, which can lead to severe legal penalties and sanctions.
Failing to properly preserve data can cripple your legal defense before it even begins. By establishing a clear, repeatable process for initiating and managing holds, you ensure that crucial evidence is protected and that your organization can respond to legal challenges with integrity and confidence. This transforms a high-stakes, reactive scramble into a controlled, compliant procedure, providing invaluable peace of mind during stressful times.
How to Get Started
Your legal hold process should be a clearly defined protocol that can be activated immediately when a “trigger event” occurs, such as receiving a subpoena or a credible threat of a lawsuit. The procedure should identify who is responsible for initiating the hold, how it will be communicated, and which documents and data sources are included.
- Example 1 (Corporate): A company receives a demand letter from a former employee alleging wrongful termination. The legal department immediately issues a hold notice to the employee’s former manager, HR personnel, and IT, instructing them to preserve all emails, performance reviews, and digital communications related to the employee.
- Example 2 (Financial Services): A financial institution is notified of a regulatory investigation by the SEC. It activates its pre-defined legal hold protocol, which automatically suspends the deletion of all trading records, client communications, and internal audit reports for the specified time period and individuals under investigation.
Key Insight: A legal hold isn’t just a suggestion; it’s a legally enforceable obligation. Integrating this into your document retention policy best practices ensures your organization is prepared to act decisively and defend its interests without risking non-compliance.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
- Create Pre-Drafted Notices: Have legal hold notification templates ready to go, so you can issue them quickly and clearly to all relevant employees (custodians).
- Identify Key Data Sources: Proactively map where critical information is stored, including email servers, cloud storage, local hard drives, and messaging apps.
- Train Employees on Requirements: Regularly train staff on what a legal hold is, their personal responsibility to comply, and the serious consequences of non-compliance.
- Document Everything: Keep meticulous records of all hold-related activities, including who was notified, when they were notified, and their acknowledgment of the hold.
8. Establish Secure Destruction and Data Disposal Standards
A document retention policy is incomplete without a plan for what happens when a document reaches the end of its life. Secure destruction is the final, critical step that ensures sensitive information doesn’t fall into the wrong hands after its retention period expires. This process involves using certified, irretrievable methods to dispose of both physical and digital records, protecting your business from data breaches, identity theft, and non-compliance penalties.

Simply throwing paper in the recycling bin or dragging a file to the trash is not enough. A formal destruction procedure provides a verifiable audit trail, proving you have handled sensitive data responsibly from creation to disposal. This brings peace of mind and transforms data disposal from a lingering risk into a controlled, compliant process.
How to Get Started
Begin by defining clear, written procedures for how different types of documents will be destroyed. Your standards should align with legal requirements and data sensitivity, specifying the approved methods for both physical paper and electronic media. For electronic records, ensuring physical destruction of storage media is paramount. For more on this, it’s worth reviewing the importance of Choosing Trusted Hard Drive Destruction Services to ensure data is truly unrecoverable.
- Example 1 (Healthcare): A clinic must follow HIPAA-compliant destruction methods, such as cross-cut shredding or incineration for patient files, and use data-wiping software that meets NIST SP 800-88 standards for hard drives on decommissioned computers.
- Example 2 (Finance): A firm handling credit card information must adhere to PCI-DSS standards, requiring that any stored cardholder data on paper is cross-cut shredded and any digital data is rendered unrecoverable upon disposal.
Key Insight: Secure destruction is a core pillar of document retention policy best practices. It’s not just about getting rid of old files; it’s about proving you did so in a secure, compliant, and irreversible manner.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
- Partner with Certified Vendors: Use a NAID AAA certified destruction service for sensitive paper documents and electronic media to ensure a secure chain of custody.
- Request Certificates of Destruction: Always obtain and file a certificate of destruction for every batch of disposed records. This serves as your legal proof of compliance.
- Automate Deletion Triggers: Modern cloud document management software can automatically flag or delete files once their retention period ends, reducing manual oversight and error.
- Document Everything: Maintain a detailed destruction log that records what was destroyed, when, by whom, and the method used.
Document Retention Policy: 8-Point Comparison
| Title | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases | Key Advantages ⭐ | Quick Tip 💡 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implement a Classification System | Moderate–High: taxonomy design and organization-wide adoption | Moderate: DMS/tools, records team, training time | Consistent handling; faster retrieval; lower compliance risk | Enterprises with varied data sensitivity (healthcare, finance) | Clear rules; audit readiness; storage efficiency | Start with high‑risk categories and automate tagging where possible |
| Establish Clear Retention Schedules | Moderate: legal mapping and retention matrix creation | Low–Moderate: legal counsel, documentation tools, updates | Defensible destruction; regulatory compliance; reduced liability | Regulated functions (tax, HR, financial records) | Predictable retention; reduced over‑retention risk | Consult legal, document rationale, review annually |
| Automate Document Lifecycle Management | High: system selection, integrations, rule configuration | High: software licenses, IT resources, integration effort | Scalable enforcement; fewer human errors; real‑time monitoring | Large organizations with high document volume | Efficiency; comprehensive audit trails; productivity gains | Pilot in one department; thoroughly test automation rules |
| Develop a Comprehensive Written Policy | Moderate: cross‑functional drafting and approvals | Low–Moderate: SMEs, review cycles, executive buy‑in | Organizational consistency; legal defensibility; training basis | Any organization as foundational governance | Clarifies roles; supports onboarding; enforces accountability | Use plain language, include flowcharts, assign a policy owner |
| Implement Regular Employee Training and Awareness | Low–Moderate: program design plus ongoing delivery | Moderate: LMS/training materials, trainers, tracking | Higher compliance rates; fewer accidental errors; accountability | Organizations needing cultural adoption of retention practices | Improved compliance; measurable completion; reduced incidents | Make training mandatory, track completions, use role‑specific modules |
| Conduct Regular Compliance Audits and Reviews | Moderate–High: audit design, sampling, remediation planning | High: internal/external auditors, time, remediation resources | Identifies gaps; verifies enforcement; continuous improvement | Regulated firms, pre/post‑merger, high‑risk operations | Evidence for regulators; proactive remediation roadmap | Use standard checklists; document findings and track remediation |
| Integrate Legal Hold and Litigation Support Procedures | High: rapid coordination with legal, systems for holds | High: legal, IT, hold management tools and custodial outreach | Preservation of evidence; reduced sanctions and discovery risk | Organizations facing investigations or litigation | Litigation readiness; auditable preservation trails | Pre‑draft notices; automate holds; train custodians and track status |
| Establish Secure Destruction and Data Disposal Standards | Moderate: vendor selection and destruction controls | Moderate–High: certified vendors, tracking, verification | Irreversible disposal; reduced breach and privacy risk; cost savings | Any org handling sensitive PII/PCI or regulated data | Verifiable destruction; compliance with privacy laws; lower storage cost | Use NAID/NIST standards, request certificates, and segregate sensitive items |
From Policy to Productivity: Your Next Step Towards Effortless Compliance
Navigating the landscape of document management can feel complex, but as we’ve explored, implementing robust document retention policy best practices is not just about avoiding legal trouble. It’s about transforming a core business function from a source of friction into a driver of productivity and peace of mind. This is a strategic investment in your organization’s operational health.
By embracing a structured, AI-powered approach, you escape disorganized digital folders and overflowing filing cabinets. You create a system that works for you, not against you.
Key Takeaways for Lasting Impact
Let’s recap the core pillars we’ve covered. True mastery lies in integrating these practices into a cohesive strategy:
- Classification is Your Foundation: A logical classification system (like the one we detailed for financial, legal, and operational documents) is the essential first step. Without it, even the best retention schedules will fail.
- Automation is Your Accelerator: Manually tracking document lifecycles is a recipe for error and wasted time. Automating the process with AI from intake to secure disposal ensures your policy is applied consistently without constant human intervention.
- Training Creates a Culture of Compliance: A written policy is only effective if your team understands and follows it. Regular, engaging training turns your guidelines into ingrained, everyday habits.
- Reviews Keep You Relevant: Business needs and legal requirements change. Proactive audits and regular policy reviews ensure your strategy remains compliant, effective, and aligned with your goals.
Beyond Compliance: The Real-World Benefits
Ultimately, a strong document retention policy delivers far more than just a clean audit report. It gives you back your most valuable asset: time. Instead of spending hours searching for a single contract or worrying about what to keep versus what to delete, you can focus on high-impact activities like growing your business, serving your clients, or innovating.
The goal is to shift from the reactive chaos of manual organization to a proactive state of control. When you know exactly where every critical file is, how long it needs to be kept, and that it will be securely disposed of at the right time, you achieve a level of operational tranquility that is invaluable. This structured approach directly combats the stress and inefficiency of paperwork, paving the way for enhanced productivity and giving you back your peace of mind.
Ready to turn these best practices into reality without the manual effort? Fileo uses AI to automatically name, categorize, and file your documents within your existing cloud storage, making it simple to implement and manage your new retention strategy. Try Fileo today and experience the power of effortless organization and compliance.